The world of Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) has seen significant advancements in recent years, with the emergence of new protocols challenging the long-standing dominance of established ones.
Among these innovations, the introduction of WireGuard has generated significant interest and discussion within the cybersecurity community. This article explores into the latest advancements in VPN protocols, offering an in-depth comparison between WireGuard and OpenVPN.
Background
OpenVPN
OpenVPN, introduced in 2001, has served as the gold standard for VPN protocols for nearly two decades. This open-source software employs VPN techniques to establish secure point-to-point or site-to-site connections. OpenVPN’s long-standing popularity and extensive adoption are due to its flexibility, reliability, and capability to bypass firewalls and Network Address Translators (NATs).
WireGuard
WireGuard, in contrast, is a relatively recent entrant in the VPN protocol field. Launched in 2018, WireGuard was created to be a faster, simpler, and more modern VPN protocol. It aims to overcome some of the limitations of existing protocols like IPSec and OpenVPN by utilizing cutting-edge cryptography.

Speed Comparison
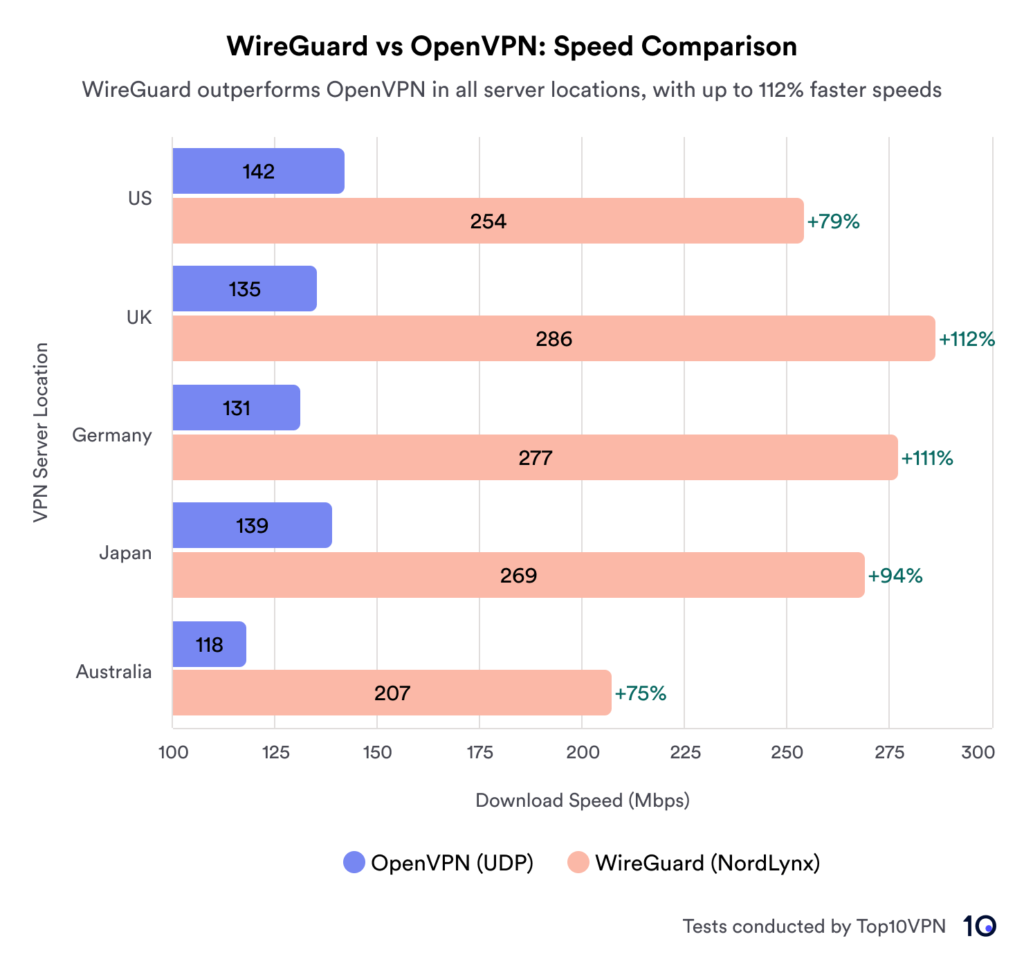
One of WireGuard’s most notable advantages over OpenVPN is its superior speed. Designed with performance as a priority, this focus is evident in various speed tests. According to tests by top10vpn, NordVPN and WireGuard (implemented as NordLynx) consistently outperformed OpenVPN across different server locations.
- US: WireGuard was 79% faster (254Mbps vs 142Mbps for OpenVPN)
- UK: WireGuard was 112% faster (286Mbps vs 135Mbps)
- Germany: WireGuard was 111% faster (277Mbps vs 131Mbps)
- Japan: WireGuard was 94% faster (269Mbps vs 139Mbps)
- Australia: WireGuard was 75% faster (207Mbps vs 118Mbps)
These results show that WireGuard is consistently over 75% quicker than OpenVPN, regardless of the server location.The speed advantage of WireGuard can be attributed to several factors:
- Optimized use of multiple processor cores
- Faster encryption methods
- Simplified codebase leading to more efficient processing
It’s important to highlight that WireGuard also establishes connections significantly faster than OpenVPN. A study by Ars Technica revealed that while an OpenVPN connection can take up to 8 seconds to initiate, WireGuard connections take only about 100 milliseconds.

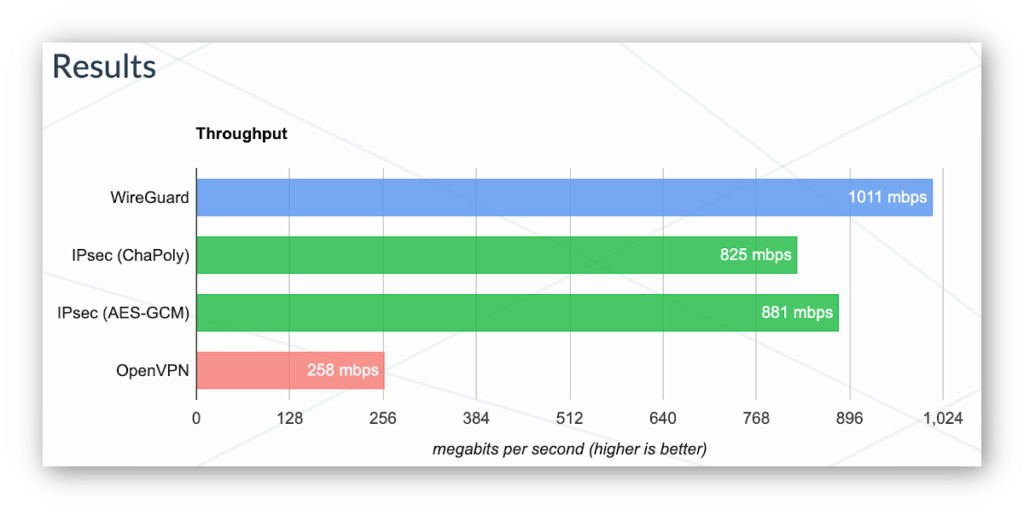
Encryption and Security
Both WireGuard and OpenVPN offer robust security features, but they approach encryption differently.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN utilizes the OpenSSL library and supports a broad array of cryptographic algorithms. It commonly employs AES-256-GCM for data encryption, which is regarded as highly secure. OpenVPN’s flexibility enables it to be configured with various encryption levels, making it adaptable to different security requirements.
WireGuard
WireGuard utilizes more modern cryptographic primitives, including ChaCha20 for symmetric encryption, Poly1305 for authentication, Curve25519 for key agreement, and BLAKE2s for hashing. While these algorithms are considered cutting-edge and highly secure, WireGuard’s encryption is not as configurable as OpenVPN’s. Both protocols are deemed secure when properly implemented, but OpenVPN’s longer track record and more extensive auditing history give it a slight advantage in terms of proven security.
Auditability
One of WireGuard’s major advantages is its simplicity and ease of auditing. WireGuard’s codebase is around 4,000 lines of code, compared to OpenVPN’s 70,000 lines. This significant difference in code complexity makes WireGuard much easier to audit for potential vulnerabilities. The simplicity of WireGuard’s code not only facilitates auditing but also reduces the potential attack surface, with fewer lines of code meaning fewer opportunities for bugs or vulnerabilities to exist.
Here are several key aspects how auditability of WireGuard differs significantly from OpenVPN:
- Code Size: WireGuard features a compact codebase of approximately 4,000 lines, in contrast to OpenVPN’s extensive 70,000+ lines. This substantial difference in code complexity makes WireGuard significantly easier to audit for potential vulnerabilities.
- Simplicity: WireGuard’s codebase is not only smaller but also simpler and more streamlined. This simplicity enhances the ability of security experts to thoroughly review and comprehend the code.
- Attack Surface: With fewer lines of code, WireGuard inherently presents a reduced attack surface. This minimized complexity means there are fewer opportunities for bugs or vulnerabilities to be hidden within the code.
- Audit Time: Due to its smaller size and straightforward structure, auditing WireGuard requires considerably less time and resources compared to auditing OpenVPN.
- Audit Frequency: The simplicity of WireGuard’s codebase facilitates more frequent and comprehensive audits. This allows for regular checks and updates to maintain security standards.
- Accessibility: Although both protocols are open-source, WireGuard’s smaller codebase makes it more accessible for a broader range of security professionals to effectively conduct audits.
These differences highlight how WireGuard’s design emphasizes simplicity and efficiency in auditability, contrasting with the more extensive and intricate codebase of OpenVPN.
However, it’s important to recognize that OpenVPN’s extensive history and widespread adoption have led to numerous audits over time, solidifying its reputation for security. While WireGuard is simpler to audit, OpenVPN has undergone more extensive real-world testing and scrutiny due to its long-standing presence in the industry.
Privacy Considerations
While both protocols can be implemented in a privacy-preserving manner, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
OpenVPN
OpenVPN has a well-established reputation for protecting privacy. Its configurable nature allows VPN providers to implement it in ways that enhance user privacy, such as avoiding the logging of connection data.
WireGuard
In its early stages, WireGuard faced criticism regarding privacy due to its handling of IP addresses. Initially, WireGuard stored user IP addresses on the server, raising concerns among privacy advocates. However, this issue has been addressed by most VPN providers through various workarounds. It’s important to note that the privacy implications of using either protocol largely depend on the VPN service’s implementation. A trustworthy VPN provider should be able to implement both protocols in a privacy-preserving manner.

Mobility and Network Changes
WireGuard shows a clear advantage when it comes to handling network changes and mobile connections. It manages network changes seamlessly, making it ideal for mobile devices that frequently switch between Wi-Fi and cellular data.OpenVPN, on the other hand, has historically struggled with network changes. When a device switches networks, OpenVPN often needs to re-establish the connection, which can lead to temporary disconnects.
Censorship Circumvention
In terms of bypassing censorship and geo-restrictions, OpenVPN currently has an edge over WireGuard. OpenVPN’s ability to use TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) as well as UDP (User Datagram Protocol) makes it more versatile in circumventing network restrictions.WireGuard, which only uses UDP, can be more easily blocked by strict network filters. However, some VPN providers are developing solutions to make WireGuard more resilient against censorship.
Device Compatibility
OpenVPN, being the older and more established protocol, currently enjoys wider device compatibility. It’s supported on virtually all platforms and can be manually configured on many devices.WireGuard, while rapidly gaining support, is not yet as universally compatible. However, it has made significant strides in this area, with support now available for major operating systems including Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, and Linux.
Implementation in VPN Services
Many leading VPN providers have begun implementing WireGuard alongside OpenVPN, giving users the choice between the two protocols. For example, NordVPN has implemented WireGuard as NordLynx, while maintaining support for OpenVPN.
The implementation of WireGuard by VPN providers often includes additional measures to address potential privacy concerns. For instance, some providers use dynamic IP address allocation systems to ensure that user IP addresses are not stored persistently on WireGuard servers.
Future Prospects
As WireGuard continues to mature and gain wider adoption, it’s likely to see further improvements and broader compatibility. Its inclusion in the Linux kernel in 2020 was a significant milestone, and similar integrations into other operating systems may follow.However, it’s unlikely that WireGuard will completely replace OpenVPN in the near future. OpenVPN’s flexibility, proven track record, and wide compatibility ensure its continued relevance. Instead, we’re likely to see both protocols coexist, with users and VPN providers choosing the most appropriate protocol for their specific needs.
Conclusion
The emergence of WireGuard represents a significant development in VPN technology. Its superior speed, simplified codebase, and modern cryptographic approach make it a compelling alternative to OpenVPN.
WireGuard excels in:
- Speed and performance
- Quick connection establishment
- Efficiency on mobile devices
- Ease of auditing and implementation
OpenVPN maintains advantages in:
- Proven security track record
- Flexibility and configurability
- Wider device compatibility
- Better censorship circumvention capabilities

Both WireGuard and OpenVPN have their strengths, and which one you choose depends on your specific needs. WireGuard is faster and more efficient, especially on mobile devices. On the other hand, OpenVPN offers greater flexibility and compatibility.
As VPN technology continues to improve, both protocols will likely get even better. The competition between WireGuard and OpenVPN is pushing innovation in the VPN industry, leading to faster and more reliable VPN connections. If you use VPNs, consider a provider that offers both protocols for flexibility. Always choose a reputable VPN service that prioritizes security and respects your privacy.
WireGuard’s development and adoption by major VPN providers represent a new era in VPN technology. While it won’t replace OpenVPN entirely, WireGuard sets a new standard for speed, simplicity, and security in modern VPN protocols.




