Imagine a world where you can surf the web with lightning speed, play online games without lag, and access your home computer from anywhere – all while keeping your identity under wraps. Sounds like a digital utopia, right?
But here’s the catch: in reality, this cyber paradise isn’t so easy to achieve. Lurking in the shadows are hackers, nosy government agencies, and cybercriminals, all eager to track your online footsteps and peek into your digital life.
To make matters worse, you might find yourself trapped behind virtual walls, unable to run your desired servers, struggling with sluggish connections, or locked out of your own data when you’re away from home.
Enter port forwarding – your secret weapon in this digital battleground. It’s like having a skeleton key for your online world, giving you unprecedented control over your devices and servers.
But beware! While port forwarding can be a game-changer, it’s not without its risks. It’s most potent when combined with other high-tech tools in your cybersecurity arsenal.
Ready to dive into the world of port forwarding? Buckle up as we explain to you its mysteries, explore its uses, and show you how to harness its power – especially when paired with a VPN. Get ready to take control of your digital destiny!

Understanding Internet Ports: How Do Internet Ports Work?
To grasp how port forwarding operates, it’s essential first to understand the concept of an internet port. Essentially, the internet employs various labels to direct online traffic to its correct destination, and a port is one such label.
Ports work in conjunction with IP addresses, which identify devices on a network. While the IP address routes data to the correct device, the port number ensures it reaches the correct application on that device. For example, HTTP traffic typically uses port 80, while HTTPS uses port 443.
Ports are crucial for cybersecurity. Firewalls use port numbers to control traffic, allowing or blocking data based on security rules. Attackers often scan for open ports to exploit vulnerabilities, making port management a key aspect of network security
What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding is a technique used in computer networks to direct data packets from one address and port to another address and port. This is usually done through a router or firewall, allowing devices inside a private network (like at home or in an office) to be accessed from outside that network. Port forwarding is often used to enable specific services like web servers, game servers, or security cameras that are behind a router.
It’s a specific application of network address translation (NAT) that plays a crucial role in directing internet traffic. When a communication request is made from one address and port number combination, port forwarding redirects it to a different address and port number combination. This redirection occurs as data packets pass through a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. Essentially, port forwarding acts as a traffic controller, ensuring that incoming data reaches its intended destination within a private network.
Basic Concepts
IP Address and Port
An IP address (Internet Protocol Address) is a unique identifier for each device connected to a network. There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 is more common and consists of four sets of numbers separated by dots, like 192.168.1.1. IPv6 is newer and has a longer, more complex format to accommodate a larger number of devices.
A port is a communication endpoint in a network protocol. Each service or application running on a device communicates through a specific port number. For example, web servers typically use port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS, while email servers might use port 25 or 587. The combination of an IP address and a port number is called a “socket,” and this is what devices use to direct data to the correct application or service.
Network Address Translation (NAT)
In private networks, like those at home or in an office, devices are usually behind a router that uses Network Address Translation (NAT). NAT is a method used by routers to map multiple local IP addresses to a single public IP address. This allows several devices in a local network to share one public IP address for communicating with the internet.
NAT helps conserve IP addresses and enhances the security of the internal network by hiding local IP addresses from the internet. However, NAT also limits the ability of external devices to access devices within the internal network, as only the public IP address is visible from the outside. This is where port forwarding plays an important role.
To better understand port forwarding, let’s explore some basic computer network concepts that form the foundation of this technique.
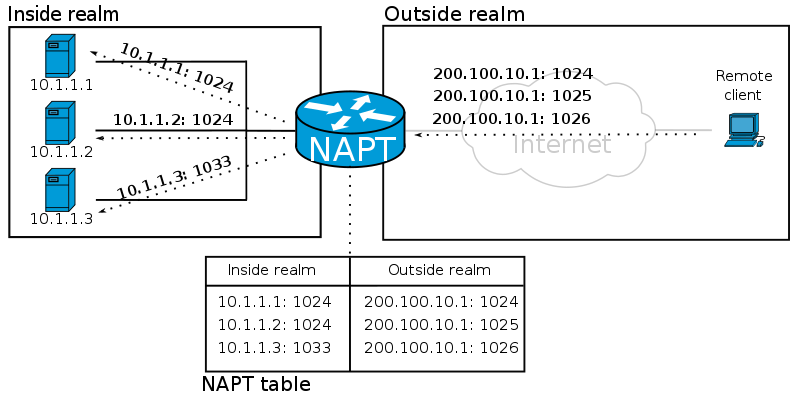
A port number specifically identifies the exact internet service you wish to access.
For instance, Port 90 is used for accessing HTML information, such as web pages that begin with “http.” Port 12 is designated for the “Film and Image Editing” service, and Port 35 is used for “Newsletter” services. In total, there are approximately 65,000 ports available on the internet.
Once a port is assigned a particular function, it generally remains unchanged. In this sense, ports are akin to television or radio channels; regardless of the device you use, you tune into the same channel number.
So, how do these ports function? When you connect to the internet, you have two different IP (Internet Protocol) addresses: a public IP address and a private IP address.
Your public IP address, assigned by your Internet Service Provider (ISP), is visible to almost anyone with sufficient technical knowledge. This address is responsible for sending and receiving information from other public IP addresses on the internet.
Other users can attempt to connect with you via this address, and depending on your browsing habits, some individuals may be able to observe your online activity by identifying the websites your public IP address has interacted with.
Conversely, your private IP address is typically not accessible to the public. Your router uses this address to direct traffic to and from specific devices within your local network.
Unlike the public IP address, a private IP address alone cannot usually establish successful connections with other websites or devices online. Instead, it sends its requests through the public IP address to retrieve information.
While your tablet, desktop, and PC would all share the same public IP address, each device would have a unique private IP address. Typically, a private IP address consists of your public IP address with additional digits appended at the end.

Port Forwarding as a VPN
Port forwarding can be used in the context of a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for various purposes, such as enabling remote access to servers or devices that are behind a private network. Here are a few ways port forwarding can play a role in a VPN setup:
Accessing Internal Servers: In a VPN setup, users may need to access internal servers or devices that don’t have a public IP address. With port forwarding, a network administrator can direct traffic from a specific port on the VPN’s public IP address to the internal IP address and port of the desired device.
Securing the Connection: Port forwarding can help enhance security by restricting access to internal devices only through the VPN connection. Only traffic that enters through the forwarded port will be sent to the internal device, reducing the risk of external attacks.
Improving Performance: In some cases, port forwarding can help improve performance by reducing latency and speeding up data transmission. This is because data can be directed straight to the desired device without having to pass through multiple network hops.
Port Forwarding with VPN
Using port forwarding together with a VPN can offer additional benefits in terms of security and flexibility. Here are a few ways port forwarding can be used with a VPN:
Remote Access: With a VPN, users can connect to a private network remotely as if they were physically present at the network’s location. Port forwarding allows users to securely access specific devices within that network, such as servers or security cameras, through the VPN connection.
Bypass Geo-Restrictions: VPNs are often used to bypass geographic restrictions on content. With port forwarding, users can direct traffic from a specific port to a server in a desired location, enabling access to restricted content.
Enhanced Security: A VPN provides an encryption layer that protects transmitted data. By adding port forwarding, users can limit access to internal devices through specific ports, adding an extra layer of security.
If you happen to be looking for a VPN, we recommend NordVPN or Surfshark as your options.
Port Forwarding with UPnP
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) is a protocol that allows devices on a network to automatically configure port forwarding on the router without user intervention. This makes network setup easier for applications that require port forwarding, such as online games or streaming apps. Here’s how port forwarding works with UPnP:
Automatic Configuration: With UPnP, devices on the network can request the router to open specific ports and direct traffic to those devices. This eliminates the need to manually configure port forwarding.
Security and Risks: Although UPnP simplifies network setup, it comes with security risks. Because UPnP allows devices on the network to open ports without additional authentication, it can be exploited by malicious devices or malware to gain access to the network.
Use in Applications: Many modern applications, like gaming consoles, streaming apps, and IoT devices, support UPnP to automate network setup. This ensures that these applications can function properly without requiring users to manually configure settings.
Port Forwarding Practical Examples
Port forwarding is a highly useful technique in computer networking, offering great flexibility and functionality by allowing devices within a private network to be accessed from outside. By understanding key concepts like IP addresses, ports, and Network Address Translation (NAT), we can grasp how port forwarding works and how to implement it for various network needs.
At its core, port forwarding directs network traffic from one IP address and port to another. In home or office networks, NAT is often used by routers to let multiple devices share a single public IP address.
While NAT enhances security by hiding local IP addresses from the internet, it also limits outside access. Port forwarding overcomes this limitation by setting up rules that direct traffic from a specific port on the public IP address to a particular device within the local network. Here are 2 practical examples of scenarios where port forwarding are mainly implemented.
Setting Up Port Forwarding for a Game Server
Imagine you have a game server at home that your friends want to access from outside your network. Here are the steps to set up port forwarding:
- Identify the Game Server’s IP and Port: For example, your game server is on the local IP address 192.168.1.100 and uses port 25565.
- Configure the Router: Log into your router settings and add a port forwarding rule that directs traffic from the external port (e.g., 25565) to the local IP 192.168.1.100 and port 25565.
- Access the Server from Outside: Share your router’s public IP address with your friends. They can access your game server using that IP address and port 25565.
Using Port Forwarding with VPN for Remote Access
Suppose you want to access your home security camera while you’re abroad. You can use port forwarding along with a VPN to do this:
- Set Up VPN at Home: Configure a VPN on your home router or server.
- Forward Port to the Security Camera: Set up port forwarding on your router to direct traffic from a specific port (e.g., 8080) to the local IP address of the security camera (e.g., 192.168.1.50) and the camera’s port (e.g., 80).
- Connect to the VPN: When you’re abroad, connect to your home VPN.
- Access the Camera Through the VPN: Use the camera’s local IP address and port to access it through the secure VPN connection.
Port Forwarding: Security and Risks
While port forwarding offers many benefits, it’s important to understand the associated security risks. Opening a port on your router means allowing external traffic into your local network. If not configured correctly, this can create opportunities for hackers or malware to access your devices. Here are some steps to reduce these risks:
- Use Uncommon Ports: Avoid using common ports like 80 or 443 that are often targeted in attacks. Choose higher, less-known port numbers to lower the chances of being attacked.
- Limit IP Access: Configure port forwarding to allow access only from specific IP addresses. This can be done through your router or firewall settings, restricting access to trusted IPs only.
- Enable Your Firewall: Ensure your router and devices have their firewalls activated. Firewalls help block suspicious or unwanted traffic, adding an extra layer of protection.
- Monitor Network Activity: Regularly monitor your network activity to spot any unauthorized access or suspicious behavior. Use network monitoring tools to quickly identify and respond to threats.
- Keep Router Firmware Updated: Always update your router’s firmware to ensure you have the latest protection against security vulnerabilities.
Port forwarding is a crucial technique in network management, allowing access to devices within a private network from outside. By understanding the basics like IP addresses, ports, and NAT, as well as how port forwarding works, users can leverage this technique to boost application performance, enable remote access, and enhance network security.
Using port forwarding alongside VPNs or UPnP can provide additional benefits, such as more secure connections and easier setup. However, it’s vital to always consider security and take steps to protect your network from potential threats. With proper configuration and regular monitoring, port forwarding can be an incredibly useful tool in managing and optimizing your computer network. If you happen to be looking for a VPN, we recommend NordVPN or Surfshark as your options.






