In the world of networking, security and speed are two crucial factors that often become the primary considerations for businesses and organizations. Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) and Virtual Private Network (VPN) are two technologies frequently used to connect geographically dispersed networks. Although both aim to secure and optimize network connections, they significantly differ in how they operate and the level of security they offer.
This article will discuss what MPLS and VPN are, the differences between them, and explore the question of whether MPLS is faster and more secure than VPN. Additionally, we will examine how a combination of MPLS and VPN can be used to create a more comprehensive network solution.
What is MPLS?
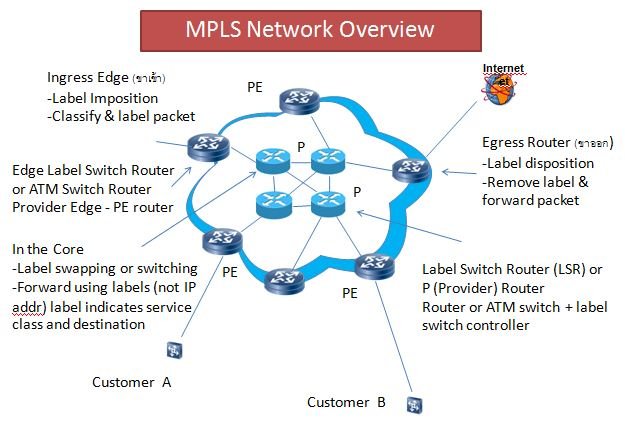
Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a network routing technique that uses labels to move data through a network. In an MPLS network, data is given a specific label and forwarded through the network based on that label, rather than the destination IP address. This allows for faster and more efficient data transmission because routers do not need to check the IP header each time data is forwarded.
How Does MPLS Work?
- Labeling: The initial router, known as the Label Edge Router (LER), assigns a label to the data packet at the beginning of the MPLS network. This label determines the path the data packet will take through the network.
- Switching: The data packet is then forwarded through a series of routers called Label Switching Routers (LSRs). These routers read the label and forward the packet based on the information in the label.
- Decapsulation: When the data packet reaches its final destination router, the label is removed, and the packet is forwarded to the actual destination IP address.
How MPLS Addresses Network Failures
MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching) addresses network failures using several effective mechanisms. Here are some of the ways MPLS handles network failures:
- Fast Reroute (FRR): MPLS uses FRR to redirect traffic to an alternative path if there is a failure in the network. FRR allows routers to redirect traffic to a pre-configured backup path, minimizing downtime and ensuring the connection remains stable.
- Path Protection: MPLS employs path protection to safeguard traffic from network failures. By doing so, MPLS can redirect traffic to a pre-configured backup path, minimizing the impact of network failures.
- Local Repair and Global Repair: MPLS combines local repair and global repair to address network failures. Local repair allows routers to redirect traffic to a closer backup path, while global repair enables routers to redirect traffic to a more distant backup path.
- Tunneling: MPLS also uses tunneling to address network failures. By doing so, MPLS can redirect traffic through a pre-configured backup path, minimizing the impact of network failures.
Benefits of MPLS
- High Performance: MPLS provides fast and efficient data transmission by reducing routing overhead.
- Reliability: MPLS offers alternative paths for data in case of network failures, enhancing connection reliability.
- QoS (Quality of Service): MPLS allows for prioritizing specific traffic, such as VoIP or video conferencing, to ensure consistent performance.
What is VPN?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that allows users to create a secure and encrypted connection through a public network like the internet. VPNs are used to connect geographically separate networks or devices in a secure manner, often for remote access or to connect company branches.
Check out our comprehensive Beginner’s Guide to VPN: Comprehensive Guide to learn everything you need to know about this powerful tool.
How VPN Works
- Tunneling: Data is wrapped in an “encrypted tunnel” that protects information as it moves through public networks.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted before being sent through the network to ensure privacy and security.
- Decryption: Data is decrypted when it reaches its destination, making it readable and usable by the receiving device.
Benefits of VPN
- Security: Encryption provides high levels of security, protecting information from eavesdropping.
- Flexibility: VPN can connect various types of devices and networks, both for remote access and connecting company branches.
- Cost-Effective: VPN uses public internet infrastructure, requiring no large investment in private network infrastructure.
Main Differences Between MPLS and VPN
| Category | MPLS | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses labels to direct data through the network based on pre-determined paths. | Uses encryption and tunneling to secure data transmitted through public networks. |
| Performance | Offers higher performance with lower latency because it doesn’t need to check the IP header each time data is forwarded. | Performance can be influenced by public network conditions and the encryption/decryption process. |
| Security | Relies on private network infrastructure that is harder for outsiders to access, but doesn’t use end-to-end encryption. | Uses end-to-end encryption to protect data from eavesdropping, but is vulnerable to attacks on public networks. |
| Cost | Generally more expensive because it uses private networks managed by service providers. | More cost-effective because it uses public internet infrastructure. |
Is MPLS Faster than VPN?
Speed is one of the key factors that distinguish MPLS from VPN. MPLS tends to be faster than VPN for several reasons:
- Reduced Routing Overhead: MPLS uses labels to direct data packets, which reduces the overhead associated with checking the IP header at each network hop. This results in lower latency and higher transmission speeds.
- Optimized Paths: MPLS allows service providers to set up optimal paths for data, ensuring that data takes the fastest and most efficient route through the network.
- QoS (Quality of Service): MPLS enables the setting of priorities for specific types of traffic, such as VoIP or video conferencing, which require consistent network performance and low latency.
On the other hand, VPN uses encryption and tunneling, which adds overhead to the data transmission process. The encryption and decryption processes can slow down connection speeds, especially if the hardware or software used is not powerful enough to handle the encryption/decryption load quickly.
Is MPLS More Secure than VPN?
Security is another crucial factor to consider when comparing MPLS and VPN. Although both offer high levels of security, they achieve this in different ways:
| Security Feature | MPLS | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Private Infrastructure | Uses private networks managed by service providers, making it harder for outsiders to access. Provides an additional layer of security compared to public networks. | Uses public networks, such as the internet, to create a secure connection between users. This setup is more accessible and cost-effective. |
| Control and Management | Service providers have full control over the network, allowing them to implement strong security measures and ensure data remains secure during transmission. | Users have control over their VPN configurations, allowing them to choose the level of security that suits their needs. This flexibility is particularly useful for remote access and site-to-site connections. |
| End-to-End Encryption | MPLS does not inherently use end-to-end encryption. Instead, it relies on other security measures like physical isolation and strong network controls. | VPN uses end-to-end encryption to protect data from eavesdropping and attacks. This ensures that even if data is intercepted during transmission, it remains unreadable without the decryption key. |
| Flexibility in Security | MPLS can be configured with various security protocols and encryption methods, allowing users to choose the level of security that suits their needs. This flexibility is particularly useful for remote access and site-to-site connections. | VPN can be configured with various security protocols and encryption methods, allowing users to choose the level of security that suits their needs. This flexibility is particularly useful for remote access and site-to-site connections. |
Combining MPLS and VPN
To enhance security and flexibility, many organizations use a combination of MPLS and VPN, known as the MPLS-VPN hybrid solution. In this configuration, MPLS provides fast and reliable network paths, while VPN offers end-to-end encryption to ensure data remains secure. Although this combination offers optimal security and performance, the cost of implementing and maintaining this hybrid solution can be very high.
MPLS-VPN Hybrid Solution
This hybrid solution leverages the strengths of both technologies to provide a robust and secure network environment. The primary benefits of using a hybrid MPLS-VPN solution compared to using VPN alone include:
➡️ Reliability and Resilience: The combination of MPLS and VPN ensures that critical data is transmitted over reliable and secure paths, while non-critical traffic can be handled by more affordable Internet-based VPNs. This hybrid model enhances the overall resilience of the network by providing multiple layers of protection and redundancy.
➡️ Enhanced Security: The combination of MPLS and VPN provides a robust security framework. MPLS ensures reliable and fast network paths, while VPN adds an additional layer of encryption, protecting data from eavesdropping and ensuring end-to-end security.
➡️ Improved Performance: By leveraging MPLS for primary network paths, data transmission is optimized, reducing latency and increasing efficiency. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring consistent and high-performance connectivity, such as VoIP or video conferencing.
➡️ Cost Efficiency: While the hybrid solution may be more expensive than using VPN alone, it offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional MPLS networks. By using public internet infrastructure for non-critical traffic, organizations can reduce their reliance on expensive MPLS networks, thereby achieving cost savings.
➡️ Scalability and Flexibility: The hybrid approach allows for the deployment of Internet VPNs alongside MPLS networks, providing scalability and flexibility. This setup is particularly useful for organizations with diverse network requirements, such as connecting small and geographically dispersed remote sites.
MPLS-VPN Hybrid Solution: Speed and Latency
Speed and latency are two critical factors to consider when choosing between MPLS and VPN. MPLS offers higher speeds and lower latency because it uses optimized, dedicated paths managed by service providers. This makes MPLS highly suitable for applications requiring high network performance and low latency, such as VoIP, video conferencing, and other real-time applications.
On the other hand, VPN may have higher latency due to its use of public networks and the data encryption/decryption process. The speed of a VPN connection can also be influenced by public network conditions and the strength of the hardware or software used for encryption. Despite this, VPNs still offer sufficient speed for many business applications, especially if a high-performance VPN is used. If you are confused of what VPN to choose, we recommend to use Nord VPN or Surfshark VPN;
Surfshark:

This budget-friendly option allows unlimited simultaneous connections, providing excellent value for families or users with multiple devices.
MPLS-VPN Hybrid Solution: Cost and Flexibility
Cost is another important factor to consider. MPLS is generally more expensive than VPN because it uses private networks managed by service providers. This involves significant infrastructure costs and high operational expenses. However, for organizations requiring high performance and reliability, investing in MPLS may be justified by the benefits gained.
In contrast, VPN is more cost-effective because it uses public internet infrastructure. This makes VPN a more affordable option for many businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises. VPN also offers greater flexibility in terms of configuration and usage, allowing businesses to easily connect various devices and networks without requiring additional, expensive infrastructure.
Specific Needs and MPLS-VPN Combination
In many cases, specific network requirements will determine whether MPLS or VPN is more suitable. For applications requiring high performance and low latency, such as VoIP and video conferencing, MPLS might be the better choice. For applications requiring high data security and flexibility, VPN might be the more appropriate solution.
However, there are also situations where a combination of MPLS and VPN, or an MPLS-VPN hybrid solution, can provide additional benefits. In this configuration, MPLS provides fast and reliable network paths, while VPN offers end-to-end encryption to ensure data remains secure. This hybrid solution offers optimal performance and security, although at a higher cost.
Implementing Hybrid MPLS-VPN Solutions
To implement a hybrid MPLS-VPN solution, organizations need to consider several key factors:
- Network Requirement Evaluation: Assessing the overall network performance and security needs to determine whether a hybrid solution is required.
- Cost Management: Calculating the total cost of implementing and maintaining the hybrid solution, including costs for MPLS and VPN.
- Network Configuration: Configuring the network to support the hybrid solution, including setting up MPLS paths and VPN connections.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Performing regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure that the network functions well and securely.
Conclusion: MPLS-VPN Hybrid Solution
Port forwarding and VPN each play a crucial role in network management, offering different solutions depending on specific needs. When considering between MPLS and VPN, several additional aspects need to be considered for a more comprehensive understanding.
Port forwarding and VPN each have their advantages and disadvantages in terms of security and reliability. MPLS offers a more reliable and fast network due to its use of dedicated paths managed by service providers. This ensures that data traffic remains consistent and latency remains low. In terms of security, MPLS networks are generally more secure due to their use of private infrastructure that is difficult for outsiders to access.
However, VPN provides higher security in terms of data protection. The end-to-end encryption used by VPN ensures that data remains safe from eavesdropping and attacks during transmission. Additionally, VPN offers greater flexibility as it can be used to connect various devices and networks, both for remote access and connecting branch offices.
Final Thoughts: Future of MPLS and VPN
In the rapidly evolving digital era, the need for secure and fast networks continues to grow. Technologies like MPLS and VPN are continually evolving to meet these demands. Innovations in encryption, network management, and security solutions are enhancing network performance and security.
For the future, the combination of technologies such as MPLS and VPN is likely to become more common, particularly for organizations requiring highly reliable and secure network solutions. Hybrid solutions can provide optimal performance and security, although at a higher cost. However, with increasing demands for data security and network performance, investing in hybrid solutions can become a more economical choice in the long run.
Choosing between MPLS and VPN is not an easy decision and should be based on the specific needs of your network. MPLS offers high performance, low latency, and high reliability, making it an ideal choice for real-time applications and those requiring consistent network performance. However, the higher cost and limitations in flexibility can be barriers for some organizations.
On the other hand, VPN offers greater flexibility and higher security through end-to-end encryption, making it a better choice for connecting geographically separated devices and networks securely. VPN is also more cost-effective and easier to implement compared to MPLS. If you need a VPN, We highly recommend to try Nord VPN or Surfshark VPN.
For organizations requiring optimal performance and security, a hybrid MPLS-VPN solution can provide the best of both technologies, although at a higher cost. Ultimately, the decision should be based on an evaluation of your network needs, budget, and priorities for security and performance. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each technology, you can make a more informed and strategic decision for your network needs. If you are looking for a VPN, we recommend to use Nord VPN or Surfshark VPN.





